CP-Carrillo Tech Talk - Part 2

Did you know we perform residual hardness studies on pistons?
A residual hardness study allows us to determine the temperatures pistons experience during engine operation. As aluminium is exposed to elevated temperatures for extended periods of time, it will progressively get softer. Sectioning a used piston and taking hardness readings allow us to map out the temperature profile. Results are used in FEAs for applying thermal profiles or comparing temperature profiles between different configurations such as piston design, oiling, tune, etc. The piston displayed was sectioned for demonstration of our process as it has not been used.




________________________________________________________________
.
A frequently asked question: “How much torque do I use to tighten my steel rod bolts”?
The answer is not as easy as you may think... There are 3 basic ways of fastening bolts: Torque, Torque Angle and Stretch.
Bolt stretch, which we recommend, is a method of measuring the bolts with a bolt stretch gauge prior to tightening and then tightening them until bolt stretches to specified amount, usually given in a small range. For example 0.0050” to 0.0070”. How much the bolt stretches, tells us how much clamp load the bolt is giving. This clamp load is what keeps the split line together, staying in the upper part of the range ensures maximum clamp load, every time. To little clamp load can result in “cap walk” and/or micro welding in the split line or worse, a failure.
Torque Angle is another method and uses a predetermined torque value and then pulling an additional predetermined angle, for example 25ftlbs and 90°. This method will consistently get you safely in a stretch range but not to the same stretch every time and will work for applications where the max stretch is not required.
Torque only should be avoided when possible. Torque is only measuring friction and many things can play into this. As you tighten the bolt over and over the amount of torque need to achieve the desired stretch reduces with each assembly, this usually evens out after about 10 tightening cycles.
Last word of advice, always use liberal amounts of a quality bolt lube on the threads and under head of the bolt.
#themoreyouknow #cpcarrillo #carrillorods #connectingrods #rods #boltstretch #torque #torqueangle #lubeitup #morethebetter #slippery #performance

________________________________________________________________
.
Did you know we uses statistical process control (SPC) studies to identify manufacturing trends, and ensure that pistons are being manufactured to our high quality standards? SPC studies provide two values - Process Potential (Cpk) and Process Performance (Cp). Process Potential (Cp) describes how much of the tolerance your process is capable of taking up if it is perfectly centered on the nominal value (middle of the tolerance). Process Performance (Cpk) considers the distance from the center of your process performance to the nearest tolerance limit. CpkU decribes how much of the upper end of the tolerance is being used, and CpkL describes how much of the lower end of the tolerance is being used. Your Cpk value is determined by taking the lowest of the CpkU and CpkL values. The higher your Cp an Cpk values the better! One easy way to visualize this is using a one lane road with rails on either side, this describes the tolerance span and its limits. If you were to hit the rails with your car you will crash, the same way you generate scrap if you produce parts outside the tolerance limits. If you were to drive a motorcycle down this road you have a very low chance of hitting the rails (high Cp), but it is easier to drift between the rails (potentially low Cpk) without crashing. On the other hand if you were to drive a semi truck down the same road you would run into different issues. Since the semi truck is much wider there is a greater chance of it hitting the rails. The semi truck has greater chance of having a low process potential (Cp) and a high process performance (Cpk), since the truck is not able to drift as easily from the middle of the road. Ideally, you want a process that generates parts as close to the nominal as possible and takes up the least amount of the tolerance span.
#themoreyouknow #cpcarrillo #cppistons #pistons #ariaspistons #carrillorods #tolerance #spc #qualitycontrol #precision #manufacturing

________________________________________________________________
.
Do you know… we strive to control our manufacturing processes with micron accuracy? To confirm our competitive advantages in design and manufacturing, parts must be validated by our quality control department. Using this feedback loop in real time on the shop floor ensures that only the highest quality parts make their way to our customers.
#themoreyouknow #cpcarrillo #cppistons #pistons #ariaspistons #carrillorods #CMM #qualitycontrol #precision #manufacturing


________________________________________________________________
.
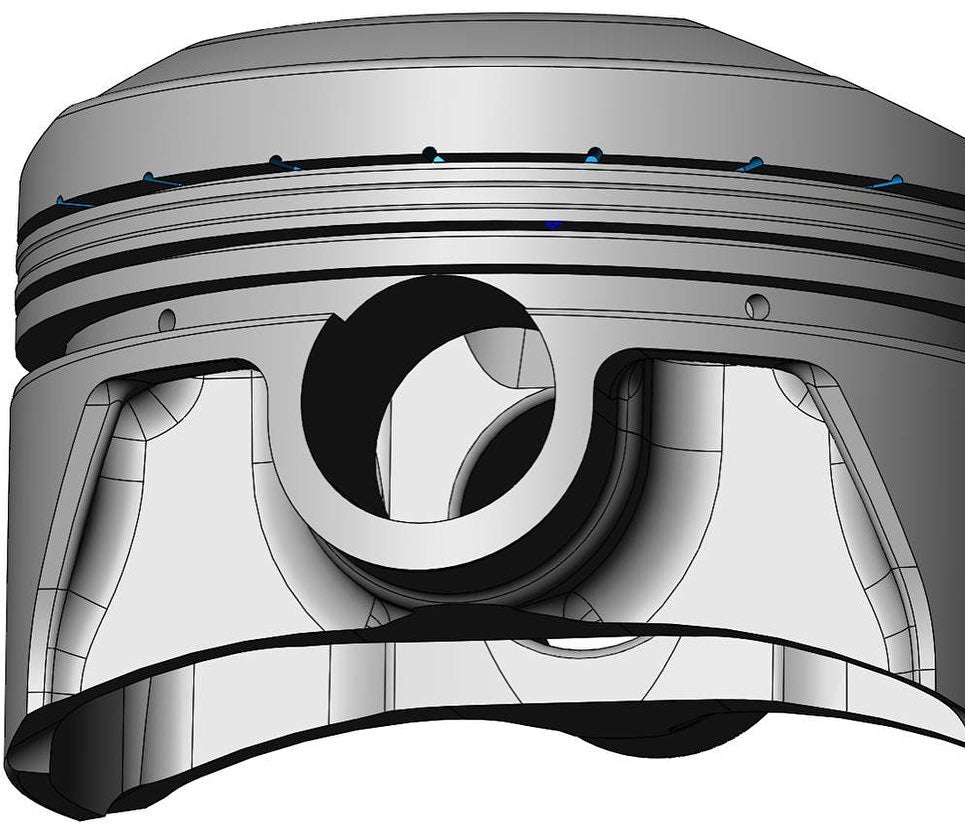
Did you know...Piston pin bores are not always manufactured to be perfect cylinders. Trumpet shapes are added to the pin bore to help distribute and reduce the peak stress and contact load on the pin bore. A portion of the bore is still cylindrical, but the trumpet portion only needs a drop as little as 0.001" (0.025mm) to be effective. In some cases a trumpet shaped pin bore can reduce peak stresses by 30%




________________________________________________________________
.
Piston and Rod Fitment
When supplying information for a piston order, make sure you provide dimensions on the connecting rod that will be used. The measurements needed are the small end width and small end thickness above the wrist pin. These two values are necessary to make sure there is no contact between the piston and the connecting rod. It’s easy to measure, all you need is a set of calipers. There is a certain amount of clearance needed, which depends on engine type, usage and whether the connecting rod is crank guided or piston guided. If a connecting rod is guided by the piston, we manufacture minimal clearance between the piston pinbosses and the connecting rod, so they touch during operation – this enables the rod to be centered in the bore by the piston, and not guided by the crankshaft. Crank guided rods are the most common set up in the racing industry today.
This information is most needed when the compression height is short, aluminum rods are used, or if there is a lot of negative volume needed in the piston to yield the desired compression ratio. One example is taking a naturally aspirated stroker engine and changing it over to a supercharged engine and lowering the compression ratio. The naturally aspirated version was 14:1 compression and now the supercharged version will be 8.5:1. The original design required a piston volume of +8.5cc’s for 14:1 and now the piston requires -52cc’s for 8.5:1. That is using the same block, stroke and cylinder head – just changing the engine parameters for the newly added supercharger.
One way to avoid this is to use the Complete Connection offered by CP Carrillo. If the piston and rod is made by one manufacturer, you don’t have to worry about fitment, you can ensure your parts will be designed and manufactured to work together as they should. Obviously if pistons and rods are ordered at the same time, we know to verify the fitment, if you have a Carrillo Rod already and plan on using it on your CP Piston, just let your CP Carrillo Team Member know when you are ordering the pistons and give him the part number from the rod and we will do the rest.





________________________________________________________________
.
Did you know....Vertical Gas Ports are holes drilled from the top of the piston into the back of the top ring groove and perpendicular to the ring groove (First Photo).
Lateral Gas Ports are holes drilled from the OD of the top ring land, right above the top ring groove and to the back of the top ring groove (Second Photo).
The purpose of gas ports is to apply combustion pressure directly to the top ring and force the ring face firmly against the cylinder wall, for maximum sealing. When not under load, the ring is under normal tension for reduced friction. The type of gas ports, quantity and hole size depends on piston/engine application and usage.
#themoreyouknow #cpknowledge #cpcarrillo #cppistons #ariaspistons #pistons #gasports #lateral #vertical #performance #engineering #precision


________________________________________________________________.
What does the Oil Support Rail do???
Oil Support Rails (OSR) assist in applications where the pin bore breaks through the oil groove of the piston (e.g. short compression heights due to big strokes or long rod lengths), without it, the oil ring would come off the ring groove through the wristpin opening. OSR have dimples that stop them from rotating thus working as a “bridge” for the ring, these dimples ALWAYS face down and OSR under NO circumstances should touch cylinder walls.
#themoreyouknow #cpknowledge #knowledgeispower #cpcarrillo #ariaspistons #pistons #custompistons #oilrailsupport #oils


________________________________________________________________
.
Do you know the difference between a Radius vs Square slot connecting rod design? The radius slot represents the well-known and durable standard CP-Carrillo H-Beam Rod design, and a square slot allows for additional weight saving with minimum compromise of rod rigidity. Ideal for applications that are critical on meeting a low target weight. #themoreyouknow #CPknowledge #cpcarrillo #carrillorods #connectingrods #customconnectingrods #performance #design #engineering #squareslotroundhole

________________________________________________________________
.
What changes are required to engines with increased cylinder pressure (example: adding a power adder to a N/A engine)? There is a matrix of changes needed when a piston uses a power adder. Depending on the level of added power, it could change the design of the piston in its entirety. The first step after evaluation of the customer’s specs is choosing a forging. A power adder application most likely requires a different forging. If there is not a perfect forging that suits the design, there is always an option to do 3D machining (“Underhead Milling”). This allows us to use a forging that may not be perfect, but we’re able to create the geometry preferred for the application. If neither of those works, we design a billet – which gives us 100% flexibility to make it perfect in every regard.



